Electrical Basics
- Understanding electrical engineering fundamentals is crucial for anyone working with electric vehicles (EVs).
- Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Laws form the foundation of all electrical analysis, from simple circuits to complex EV systems.
- We will see how these fundamental principles correlate directly to real-world electric vehicle applications, helping you understand both the theory and its practical implementation in modern EVs.
- The automotive industry relies heavily on these basic electrical laws to design safe, efficient, and powerful electric vehicles.
- By mastering these fundamentals, you'll gain the analytical tools needed to understand everything from battery pack design to motor performance optimization.
Ohm's Law
- Ohm's Law states that voltage equals current times resistance (V = I × R).
- Discovered by German physicist Georg Simon Ohm in 1827, this simple relationship describes how electrical energy flows through conductors and forms the basis for all electrical circuit analysis.
- The physical foundation rests on electron movement.
- Voltage represents the electrical pressure that drives electron flow, similar to water pressure pushing water through pipes.
- Current measures the rate of charge flow, like water flow rate measured in liters per minute.
- Resistance represents opposition to electron flow, analogous to pipe narrowness or friction that restricts water flow.
Mathematical formulations and derivations
The three primary forms of Ohm's Law provide flexibility for different calculations:
Ohm's Law Formula in its various forms
- V = I × R (Calculate voltage when current and resistance are known)
- I = V ÷ R (Calculate current when voltage and resistance are known)
- R = V ÷ I (Calculate resistance when voltage and current are known)
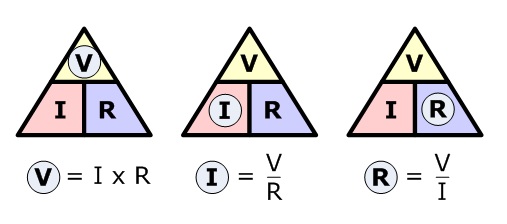
A useful memory tool is the Ohm's Law triangle.
- Draw a triangle with V at the top, I and R at the bottom corners.
- Cover the unknown variable - if the remaining variables are side-by-side, multiply them; if one is above the other, divide (top ÷ bottom).
Power relationships derived directly from Ohm's Law:
Power Formula
= (Power equals voltage times current) = =
Practical examples with step-by-step solutions
Example 1: Tesla Motor Power Analysis A Tesla Model S motor operates at 400V and draws 300A during acceleration. Calculate the motor's electrical power and equivalent resistance.
View Step-by-step solution:
- Find electrical power: P = V × I =
400V × 300A = 120,000W = 120kW - Find equivalent resistance: R = V ÷ I =
400V ÷ 300A = 1.33Ω - Verify using alternate power formula: P = V² ÷ R =
(400V)² ÷ 1.33Ω = 120,000W ✓
Kirchhoff's Laws: Comprehensive Circuit Analysis
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL): Conservation of charge
- Kirchhoff's Current Law states that the sum of currents entering any junction equals the sum of currents leaving.
- Mathematically:
= , ( is symbol for total sum of Current(I)) - Or equivalently,
= 0 (where entering currents are positive, leaving currents are negative). - The physical basis is conservation of charge.
KCL Graphical Illustration
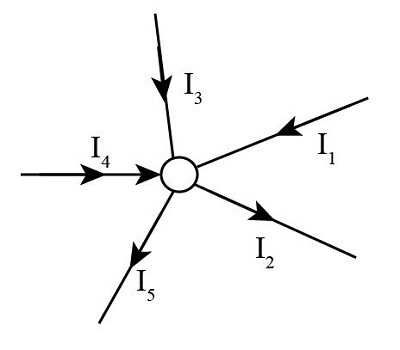
The sum of current coming into and leaving the system can be shown as,
- Since charge cannot be created or destroyed at a junction, whatever charge flows in must flow out.
- No charge can accumulate at a junction in steady-state conditions.
- Think of KCL like a water pipe junction.
- If water flows into a tee fitting from multiple pipes, the total water flow entering must equal the total water flow leaving - otherwise water would accumulate, which is impossible in steady flow conditions.
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): Conservation of energy
- Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the algebraic sum of all voltages around any closed loop equals zero.
- Mathematically: ΣV = 0, where voltage rises are positive and voltage drops are negative.
- The physical basis is conservation of energy.
KVL Graphical Illustration
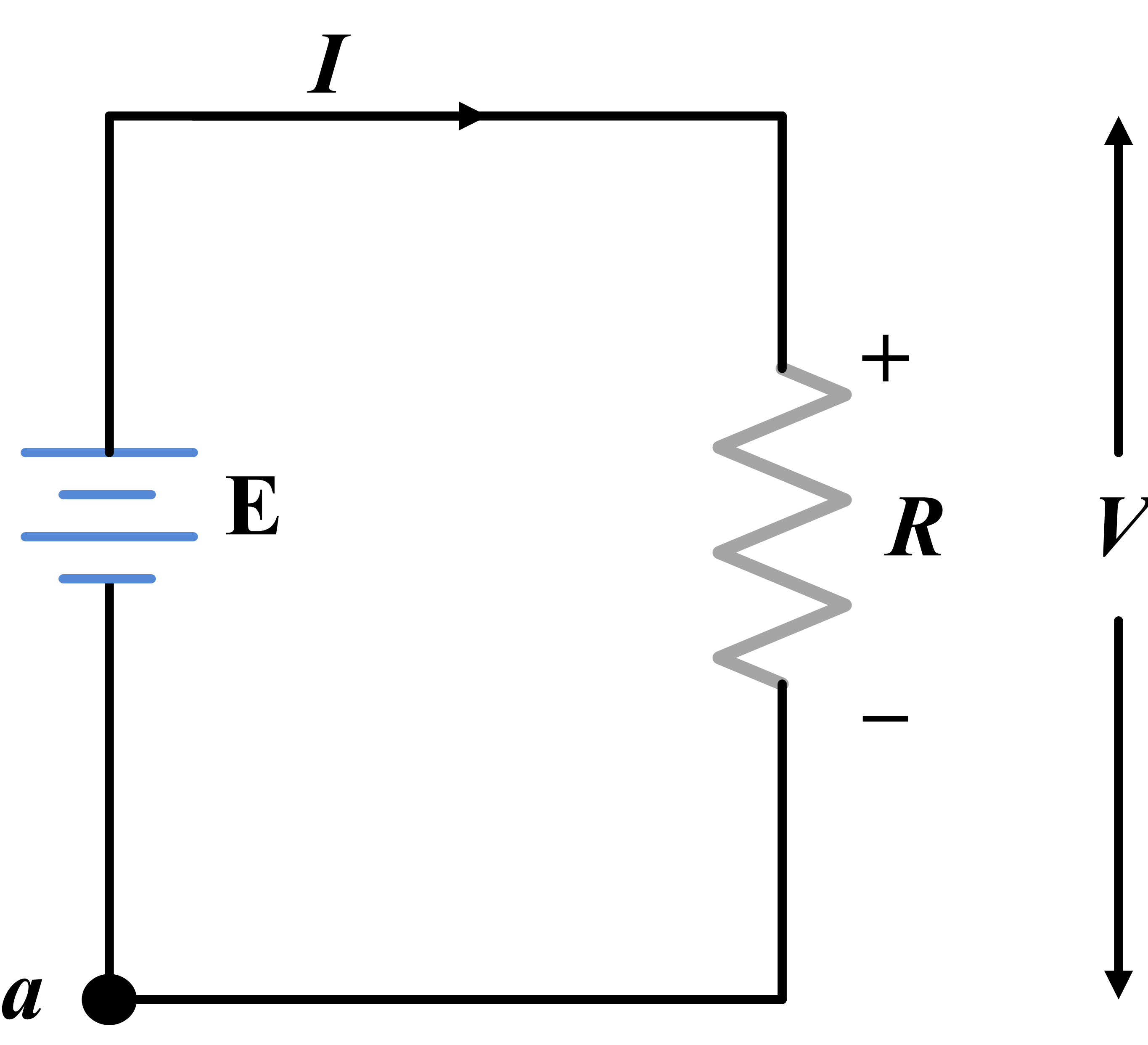
The sum of voltage supplied by power source and voltage drop caused by loads in the system can be shown as,
- When you travel around a complete electrical loop and return to your starting point, you must be at the same electrical potential.
- The total energy gained must equal the total energy lost.
- Consider the mountain hiking analogy: if you start at base camp, climb various heights, and return to base camp, your total altitude change is zero.
- Similarly, traveling around an electrical loop, voltage rises (like climbing uphill) and voltage drops (like going downhill) must balance to zero.
Systematic circuit analysis methods
Step-by-step systematic approach:
- Circuit preparation: Assign currents to every element with directional arrows. Assign voltages across components with polarity marks. Identify essential nodes (where three or more wires connect) and label them.
- Write component equations: Use Ohm's Law (V = IR) for each resistor. The current direction determines voltage polarity according to your chosen convention.
- Apply KCL: Write KCL equations at each essential node except the reference node. Number of KCL equations = (number of nodes - 1).
- Apply KVL: Write KVL equations for each independent loop. Choose consistent direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) and maintain it throughout each loop.
- Solve simultaneously: Verify that the number of equations equals the number of unknowns, then solve using substitution, elimination, or matrix methods.
- Verify results: Check that all KCL and KVL equations are satisfied and that power supplied equals power consumed.
Electric Vehicle Applications
Motor power management using fundamental laws
- Modern EV motors demonstrate sophisticated applications of basic electrical principles. Tesla's engineering team has improved motor efficiency from 80% to over 94% peak efficiency by carefully analyzing current flow, voltage drops, and power losses using Ohm's Law.
- The relationship between motor efficiency and vehicle performance is direct: an 8-10% improvement in motor efficiency translates to a 15-18% improvement in vehicle range.
- This occurs because power losses follow the I²R relationship - reducing current through improved design dramatically decreases energy waste.
Motor power calculations follow predictable patterns:
Power Calculation Formulas
- Mechanical power output:
- Electrical power input:
- Battery current draw:
Ground fault detection circuits
- They use voltage divider principles to monitor system integrity
- Normal operation: Equal voltage division indicates proper isolation
- Ground fault: Unequal voltage division triggers protective systems
- Detection sensitivity: Typically 100Ω fault resistance or lower
Safety interlock systems
- They use series-connected 12V control circuits that must remain closed for high-voltage operation.
- If any safety component opens (door, connector, service panel), the 12V circuit opens, immediately disconnecting high-voltage contactors.
Conclusion
- Motor control systems demonstrate sophisticated applications of power calculations, where efficiency improvements directly translate to increased vehicle range through the fundamental P = I²R relationship.
- Safety systems in high-voltage EVs showcase practical applications of circuit analysis, where isolation monitoring and ground fault detection protect both users and technicians.
- Charging infrastructure design requires careful load analysis using Kirchhoff's Current Law to prevent electrical service overloads
- Whether analyzing battery pack configurations, optimizing motor control algorithms, or designing charging infrastructure, these basic electrical laws remain essential tools.
- Looking toward the future, emerging technologies like 800V+ architectures, wireless charging systems, and vehicle-to-grid applications will continue to rely on these fundamental principles.
Go to Ohm's Law Calculator & Kirchhoff's Laws Series-Parallel Calculator to test your understanding and solve problems